Home > Key Stage Two > Maths > Measurement > Time > Theme Park Visit
Theme Park Times
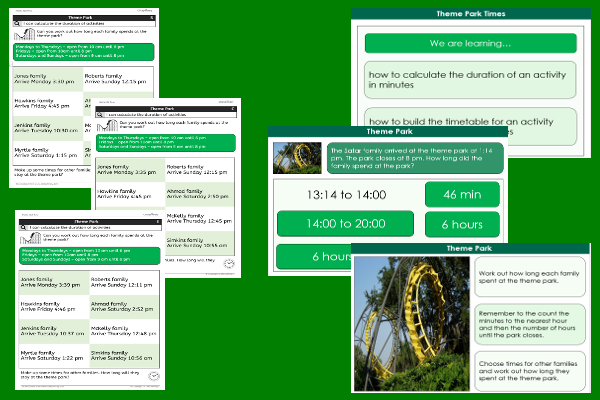
This maths teaching pack for Key Stage Two gets the children to investigate how to select and calculate the durations of family visits to a theme park using times recorded in minutes to show the total time of each visit.
The class can explain and model how to build a timetable for their own visit by adding times to show the sequence of rides experienced during the visit to a theme park.
Download this teaching pack including classroom activities and an interactive presentation to investigate how to select and calculate the durations of family visits to a theme park using times recorded in minutes to show the total time of each visit
Activities in this teaching pack include a set of differentiate worksheets to select and calculate the durations of different visits to a theme park using times recorded in minutes to identify the timing of rides experienced during each visit.
The interactive presentation gets the children to explore how to calculate the durations of family visits to a theme park using times recorded in minutes to show the timing of rides experienced.
This lesson is part of a maths scheme of work to get the children to practise identifying and calculating the timing and duration of rides and events when visiting a theme park on a special family trip. There are teaching activities for shared learning, differentiated worksheets to support independent learning and interactive presentations to introduce concepts and key skills.
-

Subtraction Differences
Explain and model some of the informal and formal written calculations skills that can be used to find the difference between pairs of two and three digit numbers
-

Fraction Equivalence
Investigate, compare and record the values of different non-unit fractions using equivalence between their sets of matching numerators and denominators
-

World Wars Poems
Explore and reflect on how poets can use figurative language and verse structures to express themes and ideas about conflicts that have happened in the world
-

Scary Tales
Investigate and replicate the structure and format of narrative stories and poetry about different spooky and mysterious people, places and events
