Home > Key Stage Two > Science > Year Three Planning > Rocks
Lesson Five – What Soils
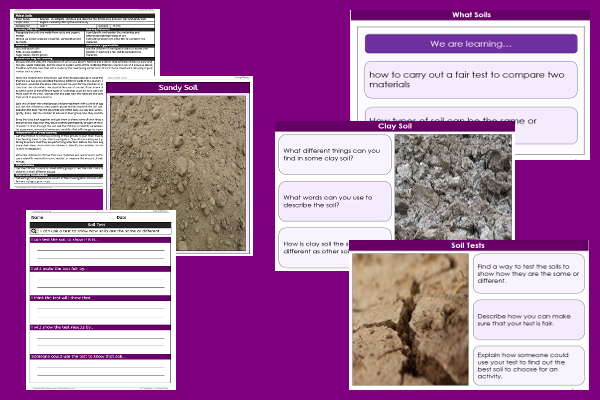
This science teaching pack for Key Stage Two gets the children to investigate, compare and describe some of the similarities and differences that can be observed between clay and sandy soils.
The class can identify and explain how to conduct a fair test to compare the two types of soils to show what makes each material special and distinct from other materials.
Download this teaching pack including a lesson plan, classroom activities and an interactive presentation to investigate, compare and describe some of the similarities and differences that can be observed between clay and sandy soils
Activities in this teaching pack include display posters to identify and describe the matching properties of different types of soil and a template to plan and conduct and investigation into the similarities and differences between clay and sandy soils.
The interactive presentation gets the children to explore how to compare and describe the some of the similarities and differences between clay and sandy soils.
This lesson is part of a science scheme of work to get the children to identify, compare and classify different types of rocks, soils and fossils according to their matching material properties for appearance, texture and substance. There are teaching activities for shared learning, differentiated worksheets to support independent learning and interactive presentations to introduce concepts and key skills.
-

Money Division
Model and record how to divide a selection of money amounts by different numbers with quotients using remainders
-
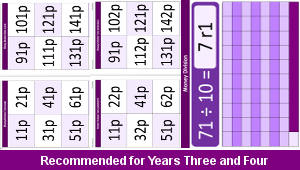
Money Division Tens
Practise selecting and dividing a range of different money amounts by ten with matching remainders in the number quotients
-

Money Division Eights
Practise selecting and dividing a range of different money amounts by eight with matching remainders in the number quotients
-

Money Division Fives
Practise selecting and dividing a range of different money amounts by five with matching remainders in the number quotients
